Machine Learning Driven Auto-tuning for Non-uniform All-to-All Collectives
Machine Learning Driven Auto-tuning for Non-uniform All-to-All Collectives
Qi, K., Fan, K., Domke, J., Ba, S., Vishwanath, V., Papka, M.E., Kumar, S.
- Location: Hyderabad, India
- PDF: ml_autotuning-3.pdf
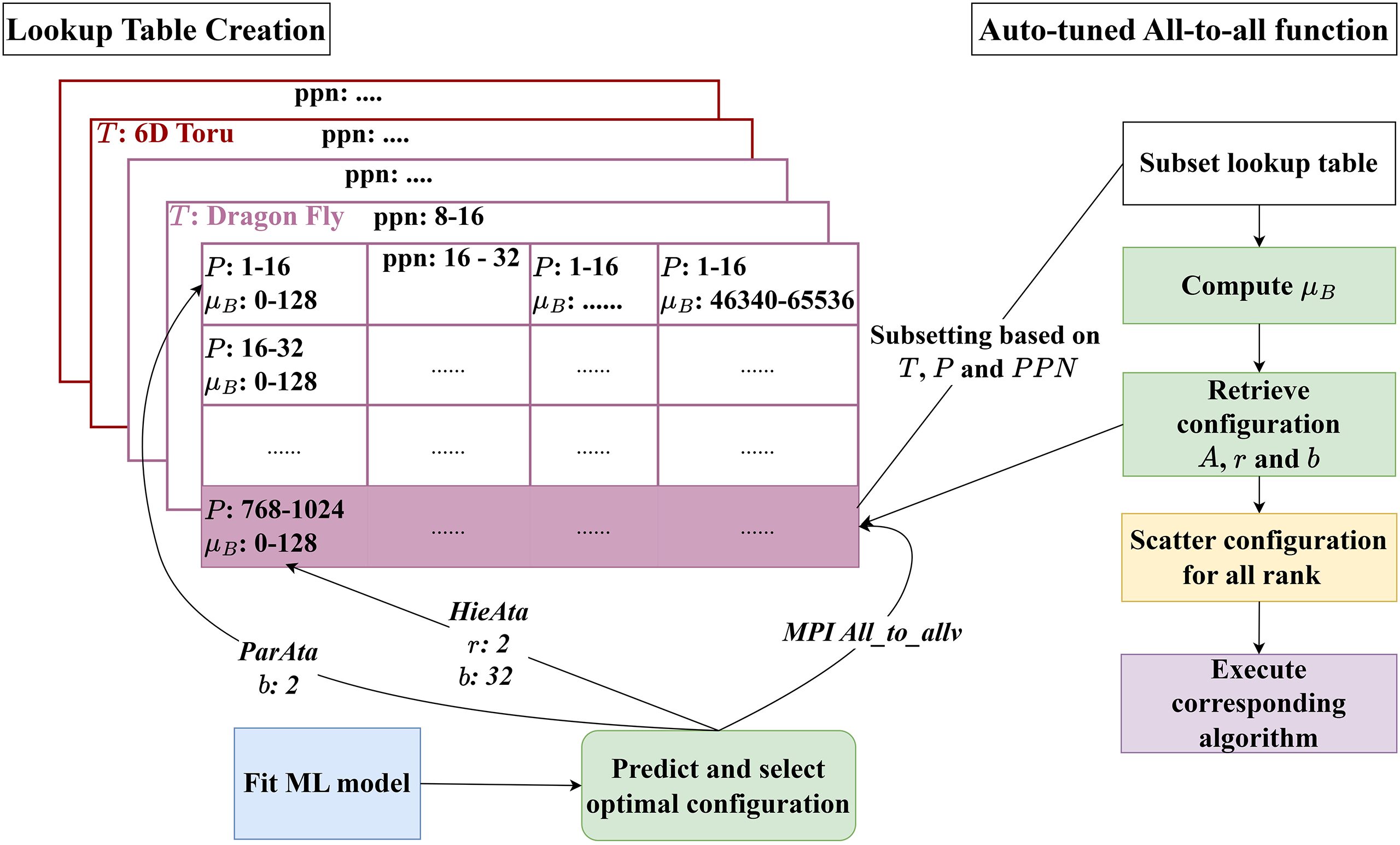
- Caption: Runtime flow of lookup table query and algorithm dispatch in the auto-tuned non-uniform all-to-all communication.
Non-uniform all-to-all communication patterns present optimization challenges in parallel computing due to their irregular data distribution and dynamic behavior. While MPI_Alltoallv provides the standard interface for such exchanges, achieving optimal performance requires careful selection among multiple implementation variants and tuning of algorithm-specific parameters. This paper presents a data-driven autotuning framework that combines machine learning–based runtime prediction with a lookup-table mechanism for fast configuration selection. The ML model estimates the communication time of each algorithm configuration under a given system setup, allowing the framework to identify the optimal implementation and parameter set based on predicted performance. We validate our approach through comprehensive benchmarking of MPI_Alltoallv and two specialized algorithms across varying process counts, message sizes, and tunable parameters. Applied to a real MPI-based transitive closure application on the Fugaku supercomputer, our framework achieves up to 6.03× reduction in communication time over he vendor implementation, providing a detailed understanding of non-uniform collective communication behavior and a practical framework for automatic performance optimization in HPC applications.
Index Terms: MPI Alltoallv, autotuning, collective communication, machine learning, sensitivity analysis